Genya Gorshtein, MSc
Published: May 9, 2023
Introduction
Antibodies (Abs) are indispensable tools in life science research and laboratory medicine, where the reliability of Ab reagents is critical to ensure reproducibility. Since monoclonal (mAb) and polyclonal (pAb) Abs are produced in vivo, they are subjected to batch-to-batch variability that may alter their binding properties and behaviours. Antibody sequencing and recombinant expression can provide robust reproducibility and unlimited supply of mAb and pAb reagents.
Hybridoma Instability Leads to mAb Irreproducibility
Hybridoma technology is one of the most widely used methods for mAb production, but they are far from problem-free. Hybridoma cell lines are created by immunizing an animal with an antigen to provoke an immune response. Ab-secreting B cells are harvested from the spleen and fused with myeloma cells to create an immortalized cell line that produces antigen-specific mAbs. Hybridomas are susceptible to several issues which can impact their reproducibility and reliability, thereby changing their behaviour for use in immunoassays and in vitro diagnostics (IVDs).
Hybridoma cell lines can be affected by contamination, either by mycoplasma or another cell type, that can significantly impact mAb production quality. Genetic drift and the appearance of additional chains can impact mAb binding properties. Evaluation of 185 hybridoma cell lines revealed that over 30% contained one or more heavy or light chains that significantly diminished the properties of the Abs, such as specificity, affinity, and avidity. Finally, hybridoma cell lines may die after cryopreservation, leading to irretrievable loss of reagents, which poses supply chain risks for immunoassays and IVDs.
Batch-to-Batch Variation in Polyclonal Antibodies
Polyclonal antibodies are known for their multi-epitope binding properties, which makes these reagents ideal for certain applications. PAbs are developed by immunizing an animal with an antigen to induce an immune response and affinity maturation processes in vivo, followed by plasma isolation and affinity purification to yield an undefined pAb mixture. Batch-to-batch variation between different lot numbers of pAb reagents is extremely common due to differences in elicited immune responses from subsequent immunizations. Additionally, the production animal eventually dies, leading to a complete loss of reagent. Recharacterization and revalidation of pAb reagents is costly and requires significant R&D efforts when the supply eventually runs out. A prominent article concerning the irreproducibility of Ab reagents even suggested that pAbs should be phased out of research entirely for these reasons. However, a well-defined cocktail of mAbs can recapitulate the binding properties of the originating pAb mixture with robust reproducibility.
Antibody Sequencing and Recombinant Expression Ensures Reproducible Antibody Reagents
To generate reproducible Ab reagents, mAbs and pAbs should be defined by their amino acid sequence using next generation sequencing (NGS) and/or next generation protein sequencing (NGPS) and expressed recombinantly (Figure 1).
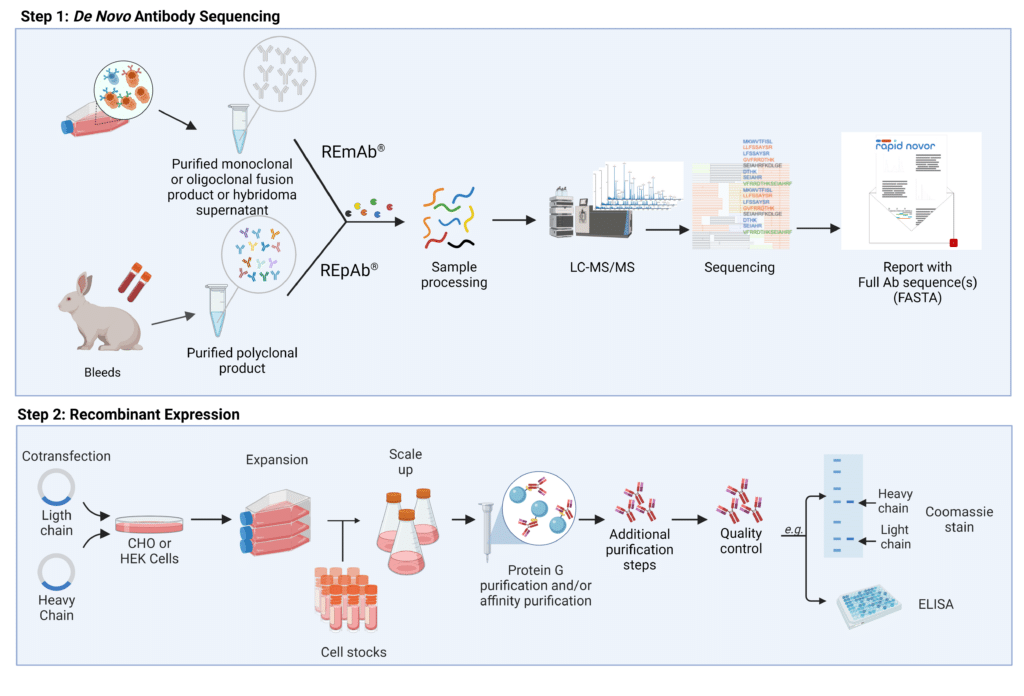
Figure 1. Steps to generate reproducible mAbs and pAbs with de novo antibody sequencing and recombinant expression. REmAb® and REpAb® can be employed to determine the sequence of full length mAbs and pAbs using LC-MS/MS. Using the amino acid information, plasmids can be created to encode heavy and light chains, and co-transfected into mammalian cell hosts that will express the desired antibody. Protein G and affinity purification, followed by quality control measures yield high-quality and reproducible rAbs defined by their amino acid sequence.
Monoclonal Antibody Sequencing
NGPS uses mass spectrometry (MS) to de novo sequence full length mAbs directly from a small sample of the protein. De novo antibody sequencing using REmAb® technology can deliver the complete Ab sequences, including complementarity determining regions (CDRs) without the need for cell lines or genomic information. De novo sequencing of mAbs using REmAb® can not only recover mAbs from lost, dead, or mutated hybridoma cell lines, but it can also replace the need for them when coupled with recombinant expression.
Polyclonal Antibody Sequencing
De novo antibody sequencing can also be applied to complex pAb mixtures to retrieve full length sequences of dominant mAbs candidates that can recapitulate the binding properties of the originating pAb. The REpAb® polyclonal antibody sequencing platform sequences antibodies starting from the serum of immunized animals, or from a purified polyclonal mixture. The derived antibody sequences can be converted into a cocktail of recombinant mAbs that recapitulate the performance of the original pAb.
Recombinant Expression
Recombinant antibody expression involves genetic engineering and expression systems to produce homogenous and high-quality Abs suitable for various applications. The first step to producing recombinant antibodies (rAbs) is to obtain the amino acid sequence of mAbs and pAbs using de novo antibody sequencing. The sequence is encoded into two plasmids for heavy and light chains, and are co-transfected into an expression system (E. coli, yeast, or mammalian cell lines) where the host cells will produce the desired Ab. Antibodies can then be purified using Protein A/G and/or affinity purification methods and characterized. Most rAbs are generated in mammalian cells, such as Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells or HEK293 cells, due to complex protein folding capabilities and post-translational modifications such as glycosylation. This in vitro method can produce high-quality rAbs that resemble Abs from the native immune system.
rAbs pose several advantages over other antibody production methods, including:
- Reproducibility: Since rAbs are defined by their amino acid sequence, they guarantee reproducibility and eliminate batch-to-batch variability.
- Scalability & high throughput production: Due to optimized production methods at high-cell densities, mammalian expression systems often exceed 12 g/L of IgG production titer.
- Animal welfare: rAbs are produced in vitro, avoiding the need for production animals.
- Highly customizable: rAbs are easily amenable to different formats (bispecifics, antibody-drug conjugates, Ab-PROTACS, etc.) and can be engineered to improve binding affinity, specificity, and stability.
Antibody and Protein Sequencing Service
At Rapid Novor, we offer an end-to-end solution for generating reproducible antibody reagents, from determining the amino acid sequence to recombinant expression, to convert your Abs to recombinant mAbs or pAbs.
- Antibody discovery service using REpAb® polyclonal antibody sequencing to convert pAbs to mAb cocktails, achieving reproducible, recombinant batches every time.
- Monoclonal antibody sequencing service to obtain the sequence of mAb reagents, to safeguard against loss and produce recombinantly.
- Peptide mapping service for antibody sequence confirmation.
To learn more about our services, inquire with our scientists.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 10,000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and developed the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 9000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables timely and reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and ran the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics