DeLuca, K. F.; Mick, J. E.; Ide, A. H.; Lima, W. C.; Sherman, L.; Schaller, K. L.; Anderson, S. M.; Zhao, N.; Stasevich, T. J.; Varma, D.; Nilsson, J.; DeLuca, J. G. Generation and Diversification of Recombinant Monoclonal Antibodies. eLife 2021, 10, e72093. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.72093.
Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies are essential reagents and research tools. They are commonly generated and produced in hybridoma cells and are expected to be highly consistent. However, the instability and fragility of hybridoma cells can cause unwanted mutations, additional chains, and permanent loss of important antibodies. On the other hand, the lack of standardization validation for commercial antibodies often keeps researchers in the dark leading to the reproducibility crisis.
Recombinant monoclonal antibodies are considered to be the most straightforward solution to circumvent the above issues with antibody production and storage. This technology also allows for antibody engineering, species switching, and production of a variety of fragments and formats. A prerequisite for antibody engineering and recombinant antibody generation is knowledge of the full amino acid sequence of the original antibody. Hybridoma sequencing and de novo protein sequencing are two technologies well-suited for this role by decoding antibody sequences from hybridoma cell lines or antibody samples, respectively. Particularly, de novo protein sequencing bypasses the generation of hybridoma cell lines and does not require any prior knowledge of nucleotide data, making it a favorable approach when cell sources are not available.
Recently published in eLife, the DeLuca lab at Colorado State University presented a step-by-step strategy for generation of recombinant monoclonal antibodies and antibody fragments. First, hybridoma sequencing and Rapid Novor’s REmAb® de novo sequencing technology were employed to derive the sequences of a series of antibodies targeting kinetochore-associated complex in the process of mitosis. The sequence data then allowed the DeLuca lab to generate recombinant forms of these antibodies, as well as to perform customization of antibody species specificity and engineering of antibody fragments including scFvC, scFv, and Fab. As a result, all recombinant antibodies and antibody fragments showed robust binding to kinetochores in mitotic cells characterized by immunofluorescence — some recombinant forms showed higher sensitivity than the commercial antibodies.
This work demonstrates a way to streamline generation of recombinant antibodies by leveraging advanced sequencing techniques. It also highlights the advantages of using recombinant antibodies including better reproducibility and manipulability. The methods developed here can be readily applied in any antibody-based research.
Graphical Abstract
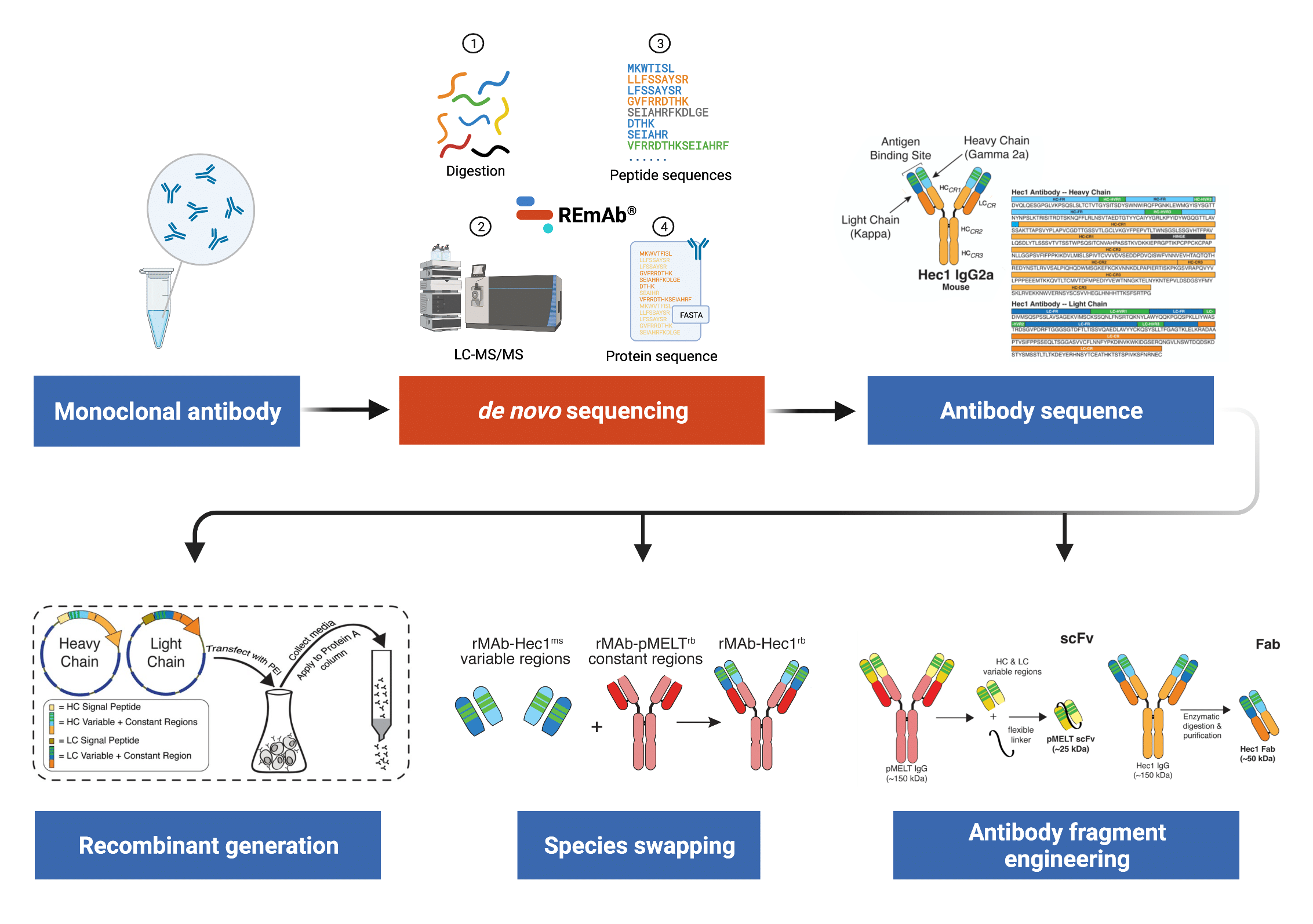
Schematic illustrating the stepwise method developed by the DeLuca lab of generating recombinant monoclonal antibodies starting with purified antibody samples. REmAb® de novo sequencing was exploited to derive the full amino acid sequence of the antibody. Knowledge of antibody sequence data can then be used for recombinant generation of the original antibody as well as engineering into a variety of formats.
Key Takeaways
- Recombinant monoclonal antibodies can avoid many problems with traditional hybridoma-based antibody preparation
- A practical methodology for generating recombinant monoclonal antibodies and antibody fragments was developed by the DeLuca lab
- De novo protein sequencing was used to determine antibody sequences from purified antibody samples; recombinant monoclonal antibodies exhibited robust binding to their target
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 10,000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and developed the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 9000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables timely and reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and ran the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics